DTN Retail Fertilizer Trends
Nitrogen Fertilizer Prices End November 2021 at All-Time Highs
OMAHA (DTN) -- Nitrogen fertilizers maintained their spot as the clear leaders as average retail fertilizer prices continued to climb higher the fourth week of November 2021, according to sellers surveyed by DTN.
Seven of the eight major fertilizers recorded considerable moves higher compared to last month. DTN designates a significant move as anything 5% or more.
Leading the way higher was anhydrous, which was up a mammoth 33% from a month prior. The nitrogen fertilizer's average price was $1,308 per ton, which continues to be all-time high in the DTN data set.
UAN32 was 26% more expensive compared to last month with the average price at $660/ton, an all-time high. UAN28 was 25% higher compared to last month with the average price of $574/ton, also an all-time high.
Urea was 16% more expensive compared to last month with an average price of $868/ton. This is also an all-time high in our data. 10-34-0 was 14% more expense looking back to last month with an average price of $755/ton.
Prices for a couple fertilizers were "only" single digits higher. Potash was 6% higher than last month with an average price of $775/ton. MAP was up 5% from last month and had an average price of $915/ton.
One fertilizer, DAP, had just a slight price increase. The phosphorus fertilizer had an average price of $830/ton.
P[L1] D[0x0] M[300x250] OOP[F] ADUNIT[] T[]
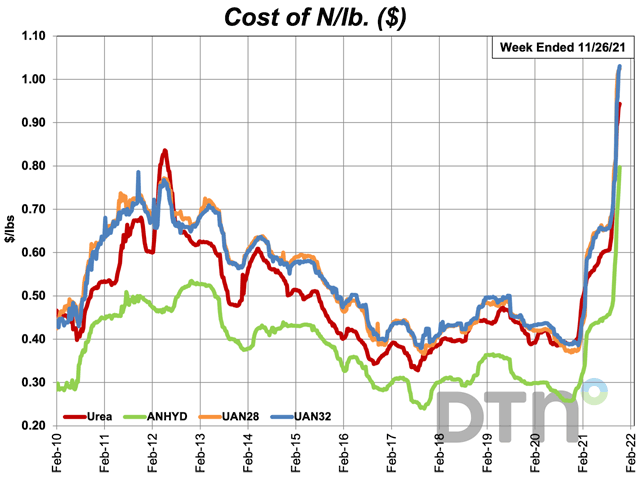
On a price per pound of nitrogen basis, the average urea price was at $0.94/lb.N, anhydrous $0.80/lb.N, UAN28 $1.02/lb.N and UAN32 $1.03/lb.N.
Last week, University of Minnesota Extension educators offered tips to become more efficient with nitrogen fertilizers. And this week, University of Missouri Extension offered similar tips with high phosphorus (P) and potash (K) prices.
In a post titled "Managing potassium and phosphorus when prices are high," University of Missouri Extension nutrient management specialist John Lory outlined a few ways producers can reduce their P and K costs (https://extension.missouri.edu/…).
Lory said farmers should not apply fertilizer to fields that are at or above optimum soil test levels. Research has found that soils at optimum soil test levels of P and K do not see increases in yield from the fertilizer applied that year.
"Why not take advantage of this benefit in a year when the price is so high," Lory asked.
If producers are not comfortable applying nothing, he suggests a second option might be to cut the fertilizer application rate by 50% or less of removal rate. Most yield responses to fertilizer is driven by the first 30% to 5% of the fertilizer applied.
Another option would be to learn more about fertilizer response. Lory suggests Missouri producers work with the MU Certified Strip Trial Program and put strips out in the field with and without P or K.
If applied to a whole field, the amount of P/K applied would drop by 50%. Strip trial program participants work with Lory and his team to document if fertilized strips have higher yield than the unfertilized strips.
"Our expectation is a field with optimum soil test will have no increase in yield on the fertilized strips," he said. "This test confirms MU Extension recommendations are working as expected on your field and contributes to a statewide effect to document fertilizer responses on Missouri farms."
Compared to a year ago, retail fertilizer prices all have increased significantly, with prices for some fertilizers increasing well over 100%.
10-34-0 is now 65% more expensive, DAP is 82% higher, MAP is 85% more expensive, potash is 130% higher, urea is 142% more expensive, UAN32 is 165% higher, UAN28 173% is more expensive and anhydrous is 208% higher compared to last year.
DTN surveys more than 300 retailers, gathering roughly 1,700 fertilizer price bids, to compile the DTN Fertilizer Index each week. In addition to national averages, MyDTN subscribers can access the full DTN Fertilizer Index, which includes state averages, here: https://www.mydtn.com/….
University of Minnesota Extension offered a top-five tips to corn producers to improve their fertilizer efficiency with high fertilizer prices. You can read it here: https://www.dtnpf.com/….
| DRY | ||||
| Date Range | DAP | MAP | POTASH | UREA |
| Nov 23-27 2020 | 456 | 495 | 337 | 359 |
| Dec 21-25 2020 | 474 | 535 | 365 | 363 |
| Jan 18-22 2021 | 493 | 563 | 379 | 387 |
| Feb 15-19 2021 | 600 | 648 | 404 | 457 |
| Mar 15-19 2021 | 616 | 693 | 424 | 496 |
| Apr 12-16 2021 | 624 | 702 | 432 | 509 |
| May 10-14 2021 | 631 | 702 | 437 | 515 |
| Jun 7-11 2021 | 656 | 717 | 450 | 527 |
| Jul 5-9 2021 | 690 | 729 | 491 | 549 |
| Aug 2-6 2021 | 695 | 755 | 557 | 556 |
| Aug 30-Sep 3 2021 | 697 | 756 | 571 | 557 |
| Sep 27-Oct 1 2021 | 722 | 800 | 647 | 620 |
| Oct 25-29 2021 | 812 | 873 | 731 | 751 |
| Nov 22-26 2021 | 830 | 915 | 775 | 868 |
| LIQUID | ||||
| Date Range | 10-34-0 | ANHYD | UAN28 | UAN32 |
| Nov 23-27 2020 | 457 | 424 | 210 | 249 |
| Dec 21-25 2020 | 463 | 461 | 210 | 250 |
| Jan 18-22 2021 | 481 | 482 | 215 | 251 |
| Feb 15-19 2021 | 522 | 530 | 245 | 288 |
| Mar 15-19 2021 | 596 | 671 | 331 | 373 |
| Apr 12-16 2021 | 609 | 700 | 345 | 387 |
| May 10-14 2021 | 620 | 713 | 361 | 406 |
| Jun 7-11 2021 | 620 | 718 | 363 | 414 |
| Jul 5-9 2021 | 624 | 732 | 371 | 421 |
| Aug 2-6 2021 | 631 | 738 | 367 | 418 |
| Aug 30-Sep 3 2021 | 632 | 749 | 371 | 420 |
| Sep 27-Oct 1 2021 | 638 | 782 | 388 | 444 |
| Oct 25-29 2021 | 663 | 982 | 458 | 522 |
| Nov 22-26 2021 | 755 | 1308 | 574 | 660 |
Russ Quinn can be reached at russ.quinn@dtn.com
Follow him on Twitter @RussQuinnDTN
(c) Copyright 2021 DTN, LLC. All rights reserved.